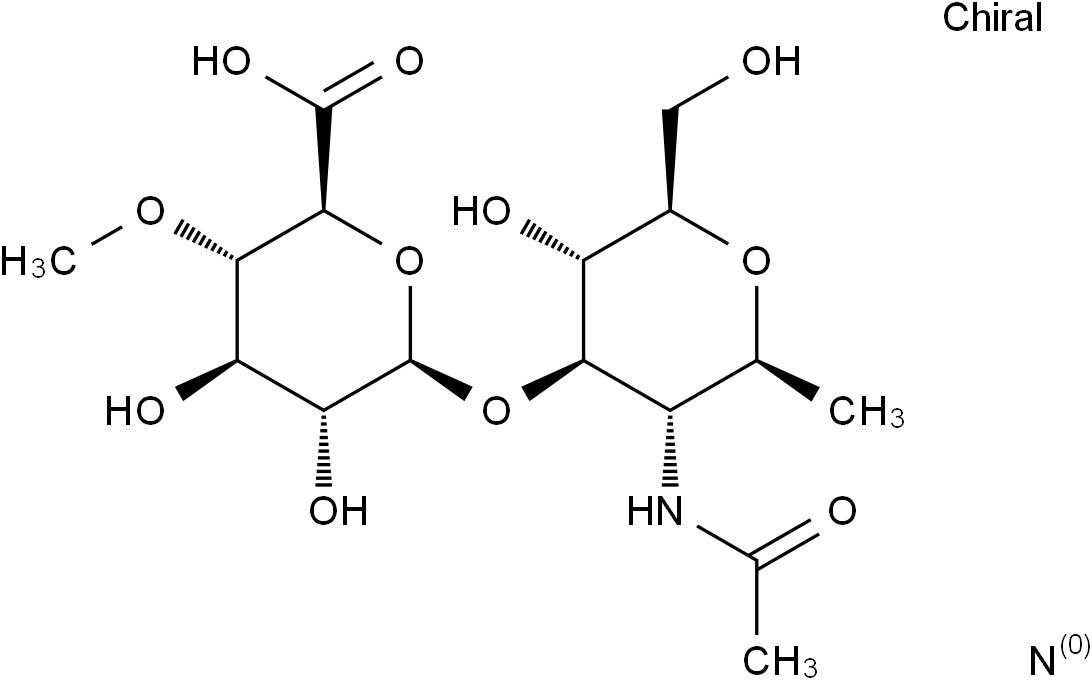
Hyaluronic acid
CAS No. 9004-61-9
Hyaluronic acid( —— )
Catalog No. M16472 CAS No. 9004-61-9
Hyaluronic Acid is a glucosaminoglycan consisting of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine disaccharide units.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 41 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 58 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 76 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 125 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 158 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameHyaluronic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionHyaluronic Acid is a glucosaminoglycan consisting of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine disaccharide units.
-
DescriptionHyaluronic Acid is a glucosaminoglycan consisting of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine disaccharide units that is a component of connective tissue, skin, vitreous humour, umbilical cord, synovial fluid and the capsule of certain microorganisms contributing to adhesion, elasticity, and viscosity of extracellular substances.(In Vitro):Hyaluronic acid (HA) is widely used in aesthetic medicine due to its binding ability with a large number of water molecules. It improves tissue hydration and their resistance to mechanical damage. HA plays an important role in wound healing, ovulation, fertilization, signal transduction, and tumor physiology. HA is used in joint diseases such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. HA of a high molecular mass reduces the chemotaxis and migration of inflammatory cells which acts as a good barrier to the inflammatory process and protects against the effects of free radicals. HA is used in ophthalmology due to its lubricating properties for the corneal endothelium, and improves tissue hydration and cellular resistance to mechanical damage in aesthetic dermatology, and has marginal adverse effects. Several trials indicate its role in tumor markers, liver diseases, and in pharmaceuticals. Hyaluronan plays an important role in cancer growth and metastasis. HA and HA fragment-tumor cell interaction could activate the downstream signaling pathways, promoting cell proliferation, adhesion, migration and invasion, and inducing angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stem cell-like property, and chemoradioresistance in digestive cancers.(In Vivo):The impact of applied intra-articular HA has been proven in many studies in animals. Studies on HA have shown that it promotes the synthesis of cartilage matrix, prevents its degradation, reduces inflammation, stimulates the synthesis of endogenous HA, and improves the resilience and moisture of cartilage . High molecular size HA preparations, applied topically, promote healing of fresh skin wounds. They also promote the healing of venous leg ulcers and are useful in the management of chronic wounds.
-
In VitroHyaluronic acid (HA) is widely used in aesthetic medicine due to its binding ability with a large number of water molecules. It improves tissue hydration and their resistance to mechanical damage. HA plays an important role in wound healing, ovulation, fertilization, signal transduction, and tumor physiology. HA is used in joint diseases such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. HA of a high molecular mass reduces the chemotaxis and migration of inflammatory cells which acts as a good barrier to the inflammatory process and protects against the effects of free radicals. HA is used in ophthalmology due to its lubricating properties for the corneal endothelium, and improves tissue hydration and cellular resistance to mechanical damage in aesthetic dermatology, and has marginal adverse effects. Several trials indicate its role in tumor markers, liver diseases, and in pharmaceuticals. Hyaluronan plays an important role in cancer growth and metastasis.HA and HA fragment-tumor cell interaction could activate the downstream signaling pathways, promoting cell proliferation, adhesion, migration and invasion, and inducing angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stem cell-like property, and chemoradioresistance in digestive cancers.
-
In VivoThe impact of applied intra-articular HA has been proven in many studies in animals. Studies on HA have shown that it promotes the synthesis of cartilage matrix, prevents its degradation, reduces inflammation, stimulates the synthesis of endogenous HA, and improves the resilience and moisture of cartilage . High molecular size HA preparations, applied topically, promote healing of fresh skin wounds. They also promote the healing of venous leg ulcers and are useful in the management of chronic wounds.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number9004-61-9
-
Formula Weight776.6
-
Molecular FormulaC28H44N2O23
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilitySoluble in Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc.
-
SMILESO[C@H]1[C@H](O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](OC)[C@@H](C(O)=O)O2)[C@@H](NC(C)=O)[C@H](C)O[C@@H]1CO.[n]
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Juhász MLW, et al. The Kinetics of Reversible Hyaluronic Acid Filler Injection Treated With Hyaluronidase. Dermatol Surg. 2017 May 10.
molnova catalog



related products
-
S-Gboxin
S-Gboxin is an active analogue of Gboxin with potent antitumour activity. S-Gboxin inhibits the growth of mouse and human glioblastoma (GBM IC50: 470 nM).
-
UDP-xylose disodium
UDP-xylose disodium is a compound that can be isolated from Cryptococcus laurentii and is a sugar donor that can be used for the synthesis of glycoproteins, polysaccharides, various metabolites and oligosaccharides in plants, vertebrates and fungi.
-
Piprozolin
Piprozolin (W 3699) is a new type of choleretic acid that shows slight analgesic properties at high doses during chronic experiments.Piprozolin has a slight induction of certain enzymes of the oxidative system.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


